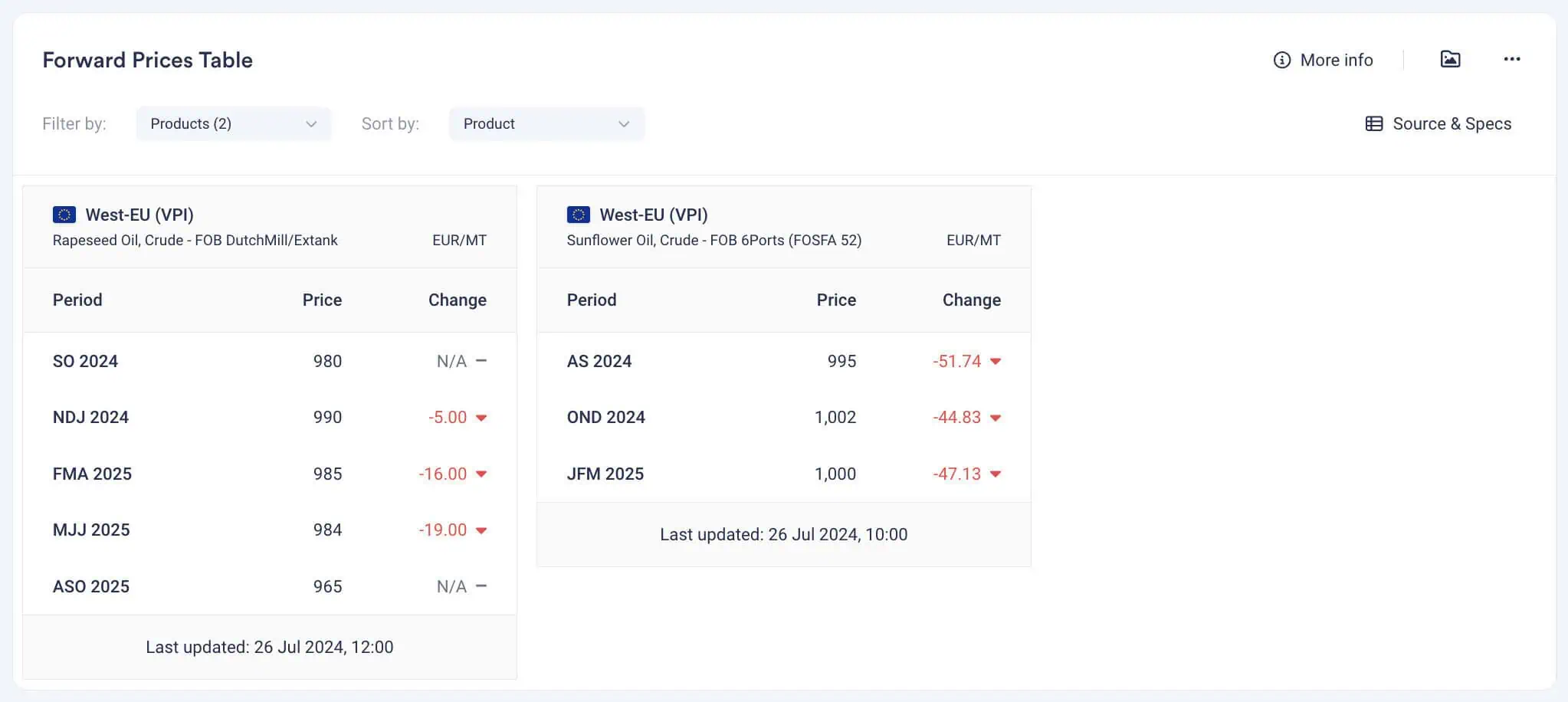
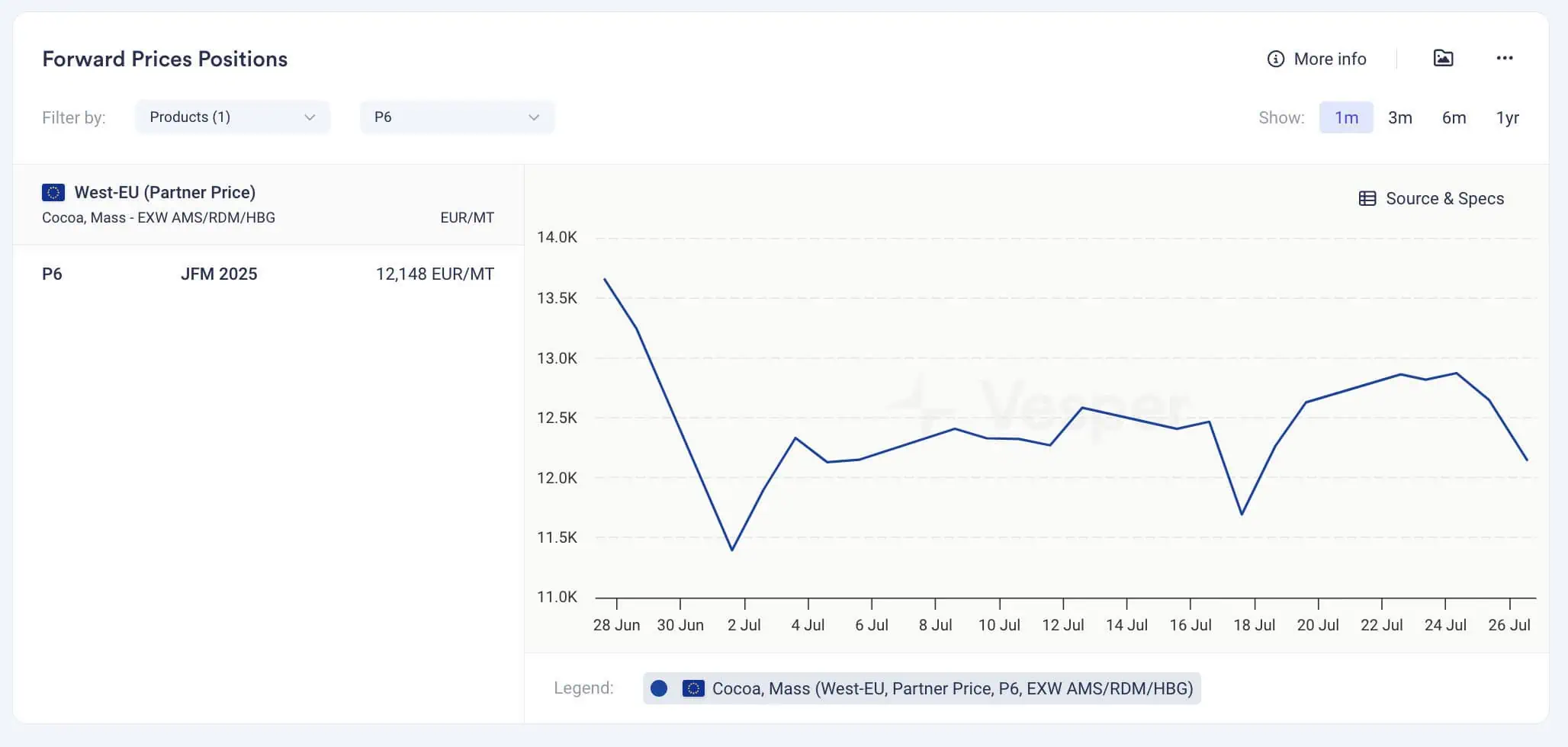
Forward prices are the agreed-upon prices for transactions that will occur at a future date. These contracts lock in prices today for delivery and payment at a later date, which could be months or even years into the future. Forward prices incorporate expectations about future market conditions and risks, such as potential changes in energy prices, logistics costs, or supply chain disruptions. This introduces a layer of complexity, as it requires an understanding of future market trends, which can be affected by numerous unpredictable factors.
Benefits of analyzing commodity forward prices
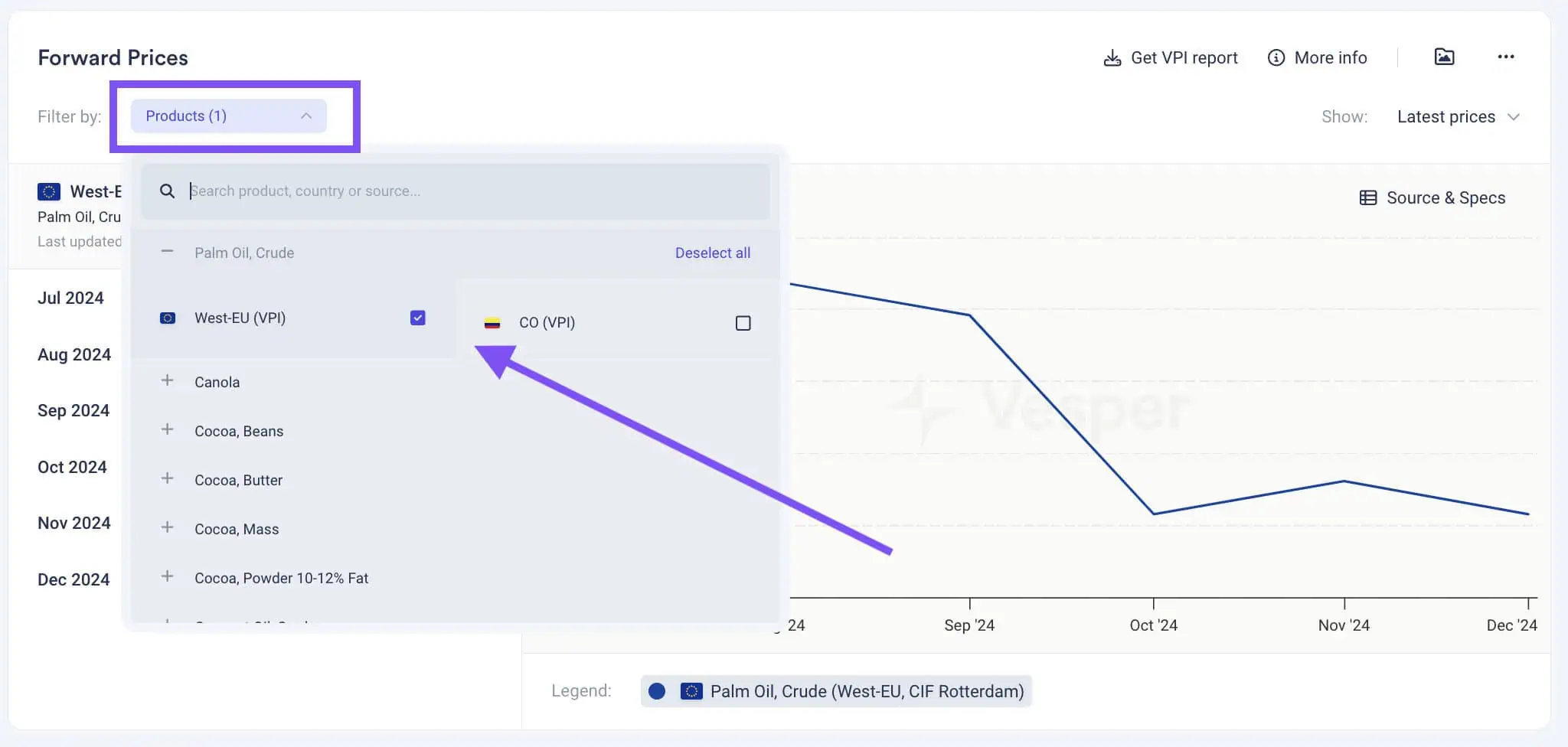
Forward Market Insights
Analysing forward prices allows market participants to anticipate market trends and price movements for future deliveries. By understanding the market expectations for purchasing products in advance with a forward delivery, businesses can plan their procurement and sales strategies more effectively. This foresight helps in mitigating risks associated with price volatility and ensures more stable financial planning.
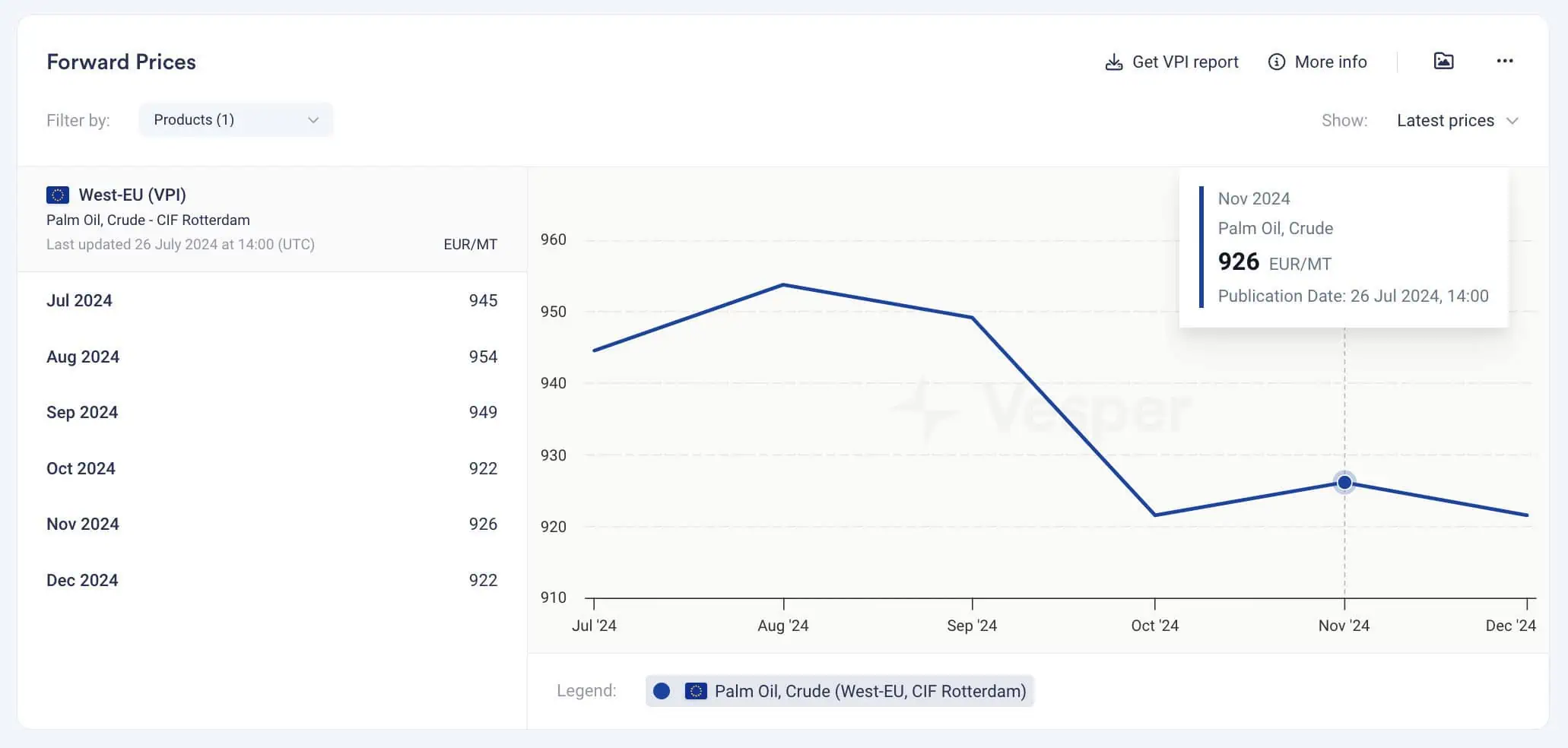
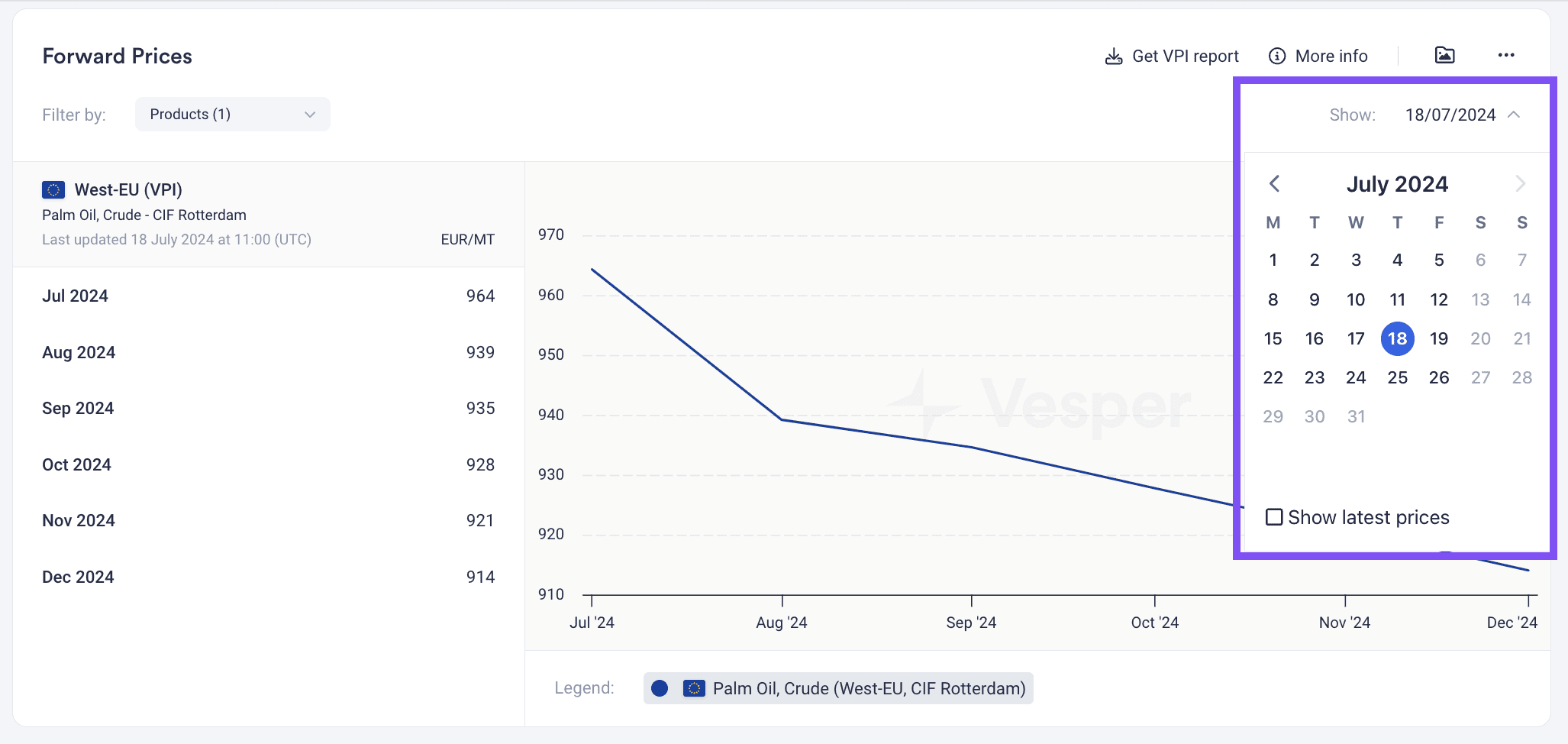
Timely Pricing Tracking
Forward pricing provides a snapshot of market prices at specific points in time, reflecting the trades completed by market participants. For volatile markets like Oils & Fats, forward pricing trades occur multiple times daily. With Vesper’s forward pricing updated up to 6 times a day, you can ensure you are analysing the most recent market prices and effectively tracking price differences over time.
Strategic Planning
Forward prices provide crucial information for long-term planning and budgeting. Companies can lock in prices for future delivery, securing supply costs and protecting against unfavourable price fluctuations. This certainty aids in better financial forecasting, cost management, and resource allocation, allowing businesses to maintain competitive advantage and operational efficiency.
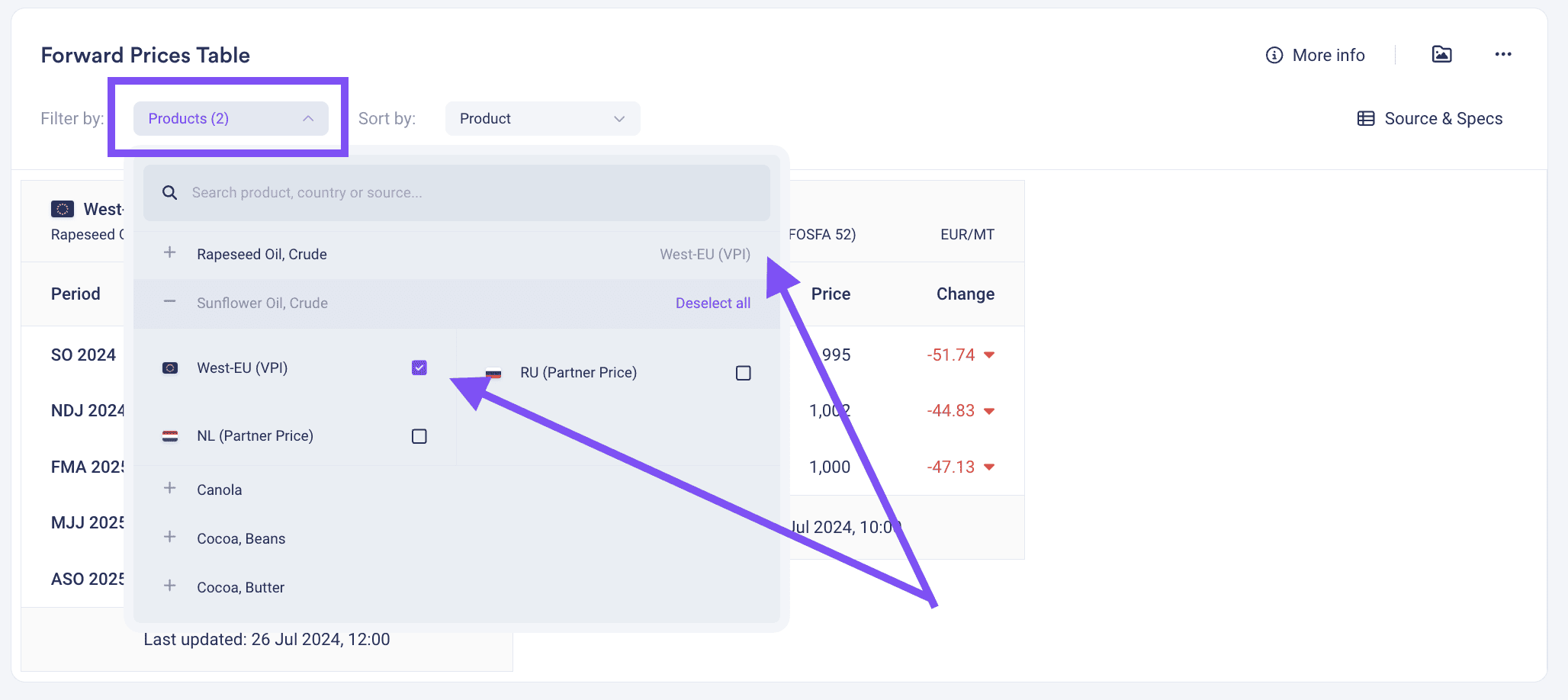
Managing Risks
Forward prices serve as a critical tool for risk management. By entering into forward contracts, market participants can hedge against adverse price movements, ensuring price stability and protecting profit margins. This ability to manage price risk is especially valuable for industries highly sensitive to commodity price changes, such as the Oils & Fats market, enabling them to safeguard their financial health in volatile markets.