In this blog, we’re going to explore the world of sugar and isoglucose in Europe, looking at how these key sweeteners are produced and how market trends are shaping their future.
As we delve into our exploration, we’ll continuously draw upon the rich sugar data from Vesper, a leading commodity intelligence platform. This approach ensures that our analysis is grounded in the most current industry data and trends, providing a solid basis for our discussions.
Our journey will take us through various aspects of the industry, including supply and demand fluctuations, export patterns, and the impact of global events.
This blog is tailored for industry stakeholders, policymakers, and informed consumers seeking a deeper understanding of these markets.
Join us as we unpack the intricacies of these sectors, presenting well-researched insights and analyses.
- Navigating Supply Trends: Understanding the Growth and Decline Dynamics
- Demand Dynamics: Interpreting Consumption Patterns in Europe
- Export Fluctuations: Reading Market Signals in Europe’s Sugar Trade
- Stock Management: Balancing Supply with Demand
- The Impact of Global Events: Learning from COVID-19
Navigating Supply Trends: Understanding the Growth and Decline Dynamics
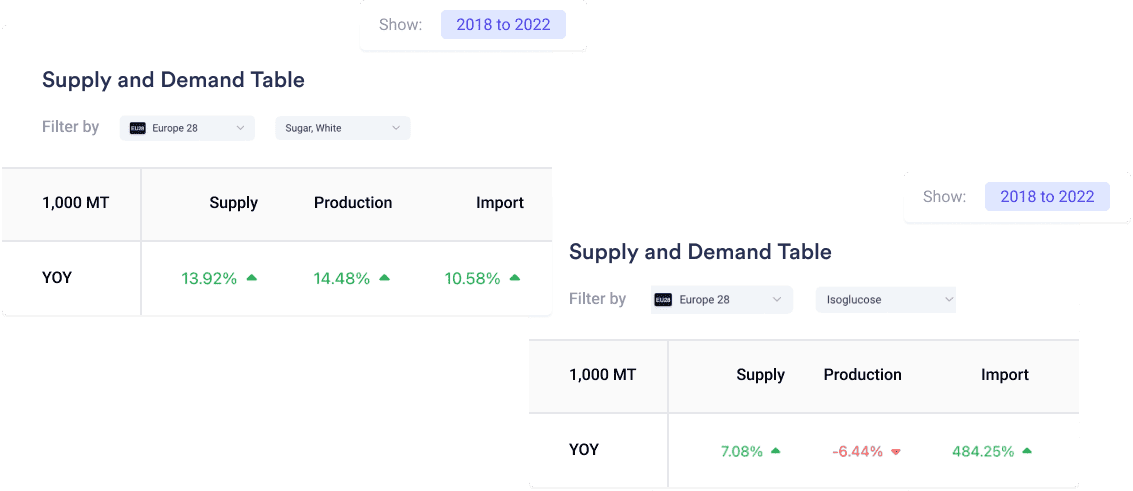
Let’s Talk About Sugar and Isoglucose Supplies in Europe!
- What’s Happening with White Sugar and Isoglucose? From 2018 to 2022, White Sugar’s supply in Europe increased by 13.92%, while Isoglucose’s supply went up by 7.08%. Interestingly, while Isoglucose imports soared by 484.25%, its production actually decreased by 6.44%.
- Why’s This Important? This trend suggests a shift in Europe towards relying more on external sources for Isoglucose, possibly due to cost factors or production challenges. For White Sugar, the slight decrease in production and high EU sugar prices may lead to a substitution for other sweeteners like Isoglucose.
- Market Dynamics: The abolition of EU quotas has intensified competition between these sweeteners. While sugar production initially surged, it’s expected to decline over time, facing lower prices and increased competition from isoglucose. Isoglucose, benefiting from deregulation, is projected to see a significant rise in consumption.
- Consumer Trends and Health Impacts: Health concerns and a push for reduced sugar content are affecting both markets. Sugar consumption is forecasted to decline, while Isoglucose is expected to gain market share.
- So, What Should You Do? If you’re a stakeholder in this market, diversifying your sweetener sources could be wise. Boosting local production or exploring alternative sweeteners might mitigate risks associated with import dependence and market shifts.
- Here’s Another Angle: Strengthening local production could lead to a more self-reliant and resilient industry in Europe, less affected by global market fluctuations and policy changes.
Demand Dynamics: Interpreting Consumption Patterns in Europe
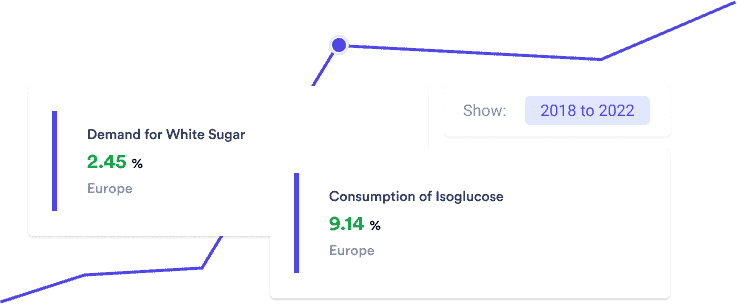
Let’s Unpack Sugar and Isoglucose Consumption Trends
- What’s Going On? Between 2018 and 2022, we’ve seen a modest increase in demand for White Sugar in Europe by 2.45%. Meanwhile, Isoglucose’s consumption is up by a notable 9.14%. That’s quite a jump!
- Digging Deeper into the Why: Why this change? It’s likely tied to how we, as consumers, are changing our eating habits and what’s happening in the economy. For instance, high sugar prices in the EU might be nudging food manufacturers to lean more towards isoglucose, especially since it’s convenient for certain products like soft drinks and ice creams.
- The Health Angle: There’s also this big wave of health awareness sweeping across Europe. The EU food industry is on a mission to cut down sugar content in food products by 10% by 2025. This trend is key to understanding why sugar consumption might remain stable or even dip despite growing supplies.
- So, What’s the Takeaway? If you’re in the business of sweet things, keep a close eye on these consumer trends. Adjusting your strategies to align with these shifts – maybe exploring low-sugar options or alternative sweeteners – could be the way to go.
- Imagine a Different Scenario: What if sugar demand was on the decline? This could signal a shift in consumer preferences, possibly due to health concerns or more folks opting for alternative sweeteners. Keeping tabs on these shifts is crucial for staying ahead in the market.
Export Fluctuations: Reading Market Signals in Europe’s Sugar Trade
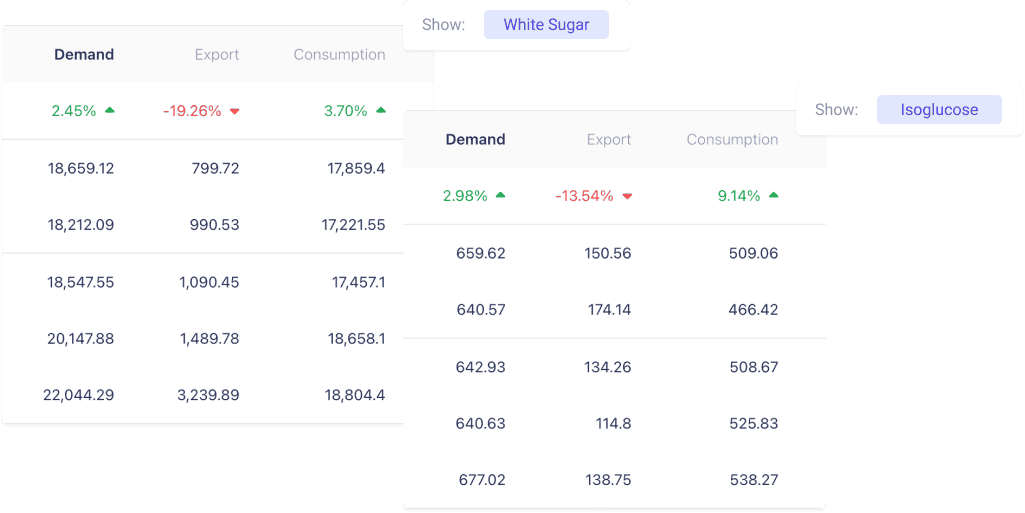
Let’s Decode What’s Happening with Europe’s White Sugar Exports
- What’s the Buzz? We’ve noticed a significant 19.26% drop in White Sugar exports from Europe between 2018 and 2022. That’s a pretty big shift, isn’t it?
- Why Is This Happening?: Several factors could be at play here. We’re talking about intense global competition, possible tariff changes, and perhaps some issues with the quality of the product. Moreover, the overall European sugar market experienced a decline in exports by about 10.7% in 2022 compared to 2021, indicating a broader trend.
- Looking at the Bigger Picture: While sugar production in the EU has seen some decrease, like the 250,000 MT dip below the 2021/22 production, the export forecast for the 2022/23 market year is stable compared to 2021/22, but still below previous years’ levels. This could suggest a realignment of the market following policy changes and shifting global demand.
- Impact of Prices and Substitution: High EU sugar prices may also be influencing this trend, potentially leading to a preference for substitutes like isoglucose. This is important because it indicates a shift in the market dynamics within the EU.
- What Should Producers Consider? Given these trends, it’s crucial for producers to look beyond traditional markets. Improving product quality, exploring value-added products, or tapping into new markets could help regain some of that lost export momentum.
- Let’s Think Differently: If exports were rising, it would signal strong international demand for EU sugar, suggesting a competitive edge in the global market. It would imply that EU sugar is favored over alternatives like isoglucose in international markets.
Stock Management: Balancing Supply with Demand
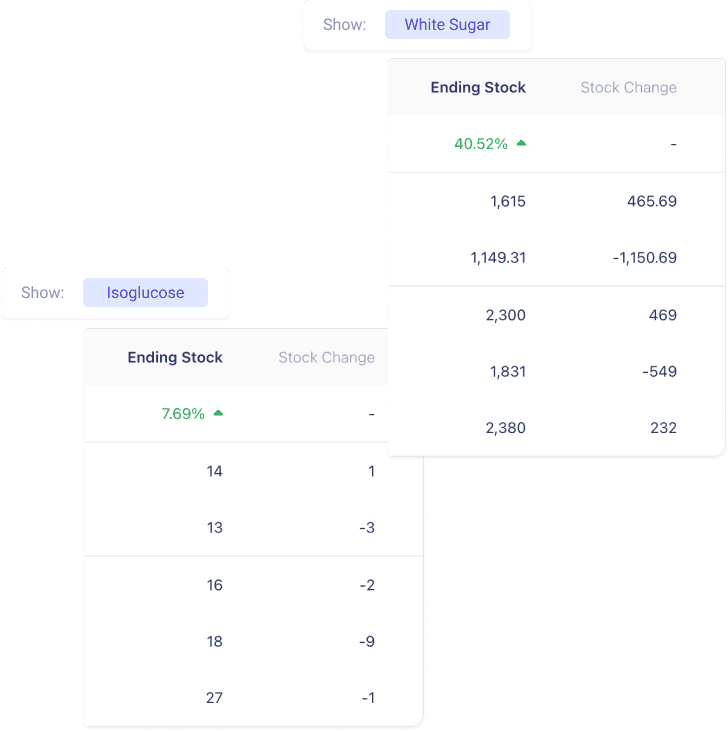
Let’s continue talking about managing sugar and isoglucose stock levels.
- What’s Up with the Stocks? From Vesper’s data, we see an increase in ending stocks for White Sugar by 40.52% and Isoglucose by 7.69%. This seems to indicate a surplus situation.
- Digging into the Reasons: So, why are these stocks piling up? There could be a few reasons like overproduction – maybe we’re making more than we need. Or, perhaps consumption is dipping, or there might be some hiccups in getting these sweeteners from factories to markets.
- The Current Scene: For white sugar, total EU production for the 2022/23 market year is forecast at 16 million metric tons, marking a decrease from the previous year. This decrease indicates that despite lower production, there’s still more sugar than needed to meet domestic consumption, leading to increased stocks.
- Isoglucose’s Side of the Story: In 2022, isoglucose sales in Europe saw a 3% decline from 2021. This decrease in sales, reflecting a trend across the EU starch industry, might contribute to rising stock levels.
- Why Good Stock Management Matters? In a surplus situation like this, managing stocks becomes crucial. Think about strategic storage and timely distribution. This helps to avoid waste and keep the market stable. If stocks are managed well, we ensure there’s always just the right amount of sweetener available when and where it’s needed.
- Imagine the Opposite: If stock levels were falling, that would be a sign of a tight market. Maybe demand is outstripping supply, or we’re not producing enough. In such cases, ramping up production or boosting imports might be necessary to keep up with the demand.
The Impact of Global Events: Learning from COVID-19
Let’s see now how COVID-19 Impacted Sugar and Isoglucose.
- What Happened During COVID-19? The pandemic shook things up, didn’t it? For White Sugar, the highest production was recorded in 2018, pre-COVID. After that, things seemed to stabilize. This pattern shows just how big global events like a pandemic can impact market dynamics.
- Why This Change? During COVID-19, we saw supply chain disruptions, changes in how we buy and consume food, and economic challenges. These factors collectively influenced the sugar market. For instance, EU sugar consumption showed a slight recovery after the COVID-19 induced decrease, suggesting how consumer behavior changed during the pandemic.
- The Bigger Picture: It’s not just about production levels. High EU sugar prices may lead to a preference for alternatives like isoglucose. But here’s the catch – the prices for wheat and corn, key ingredients for isoglucose, have also risen. This complexity adds another layer to understanding the market’s response to global events.
- So, What Can We Learn? These times call for building a resilient supply chain. Being adaptable and ready to pivot in response to global shocks is key for long-term stability in the sugar industry.
- Consider an Alternate Scenario: Imagine if production had kept increasing despite the pandemic. That could have led to a major oversupply, crashing prices, and financial strain. Balancing production with actual demand, especially during unpredictable times, is crucial.
The Impact of Global Events: Learning from COVID-19
As we conclude our in-depth exploration of the European sugar and isoglucose markets, it’s evident that these industries are shaped by a variety of significant factors.
From global events like the COVID-19 pandemic to shifts in consumer behavior and regulatory changes, each aspect plays a crucial role in determining market dynamics.
Understanding these multifaceted trends is essential for stakeholders, whether involved in production, policy-making, or consumption.
The future of these markets promises continued evolution, and we remain committed to providing up-to-date and comprehensive analysis.
Stay tuned for more insights and updates in the ever-changing world of sugar and isoglucose.Want to access proprietary and unbiased data on more than 1900+ products? Create a free account and discover the power of commodity intelligence.



