Poultry spot prices are essential indicators for producers, traders, and consumers, as they directly impact the cost and availability of various poultry products. In the dynamic poultry market, several factors can cause fluctuations in spot prices, from feed costs to consumer trends and trade regulations. Understanding the key drivers behind these fluctuations helps industry professionals make more informed decisions.
Importance of Spot Prices in the Poultry Market
Spot prices are critical for several reasons:
- Traders: They provide real-time data that helps traders make timely buy or sell decisions.
- Producers: Poultry farmers and producers can use spot prices to determine the best time to sell their products to maximise revenue.
- Buyers: Buyers, such as food manufacturers, retailers, and wholesalers, rely on spot prices to optimise their procurement strategies and control costs.
- Market Analysts: Spot prices offer valuable insights into current market conditions, aiding analysts in forecasting future trends and advising stakeholders effectively.
What Are the Key Drivers Behind Fluctuations in Poultry Spot Prices?
Poultry spot prices are influenced by various supply and demand factors, including:
- Feed Costs: Since feed represents a significant portion of production costs, fluctuations in feed prices—mainly corn and soybeans—can have a substantial impact on poultry prices. Higher feed costs generally result in increased poultry prices as producers pass on these costs to consumers.
- Disease Outbreaks: Poultry diseases, such as avian influenza, can devastate poultry supplies. In the event of a disease outbreak, many producers may have to cull large numbers of birds, leading to a sudden drop in supply and corresponding price spikes.
- Consumer Trends: Rising consumer demand for organic, free-range, and antibiotic-free poultry has created a niche market. These premium products often come with higher production costs, which drive up spot prices compared to conventional poultry products.
- Government Regulations: Stringent regulations on poultry production, such as restrictions on antibiotics or welfare standards, can raise production costs and ultimately impact spot prices.
- International Trade and Tariffs: Trade policies and agreements between countries can influence the availability and price of poultry. Tariffs or trade restrictions may reduce the supply of imported poultry or increase the costs for domestic producers.
Impact of Feed Prices and Disease Outbreaks on Poultry Spot Prices
Feed costs have consistently been one of the largest influences on poultry spot prices. Since poultry is heavily reliant on corn and soybean-based feed, any disruptions in the supply of these commodities can send ripples through the poultry market. For instance, droughts in key producing regions or geopolitical tensions can limit feed supplies and drive up prices, leading to increased poultry spot prices.
Similarly, disease outbreaks like avian influenza have the potential to severely disrupt the poultry market. In regions heavily affected by outbreaks, such as in Europe or Asia, prices tend to increase as supply diminishes. Governments may impose bans on affected areas, further limiting the available supply of poultry in the market and pushing prices higher.
In 2021 Feed Price Surge and Poultry Costs
In 2021, the global prices of corn and soybeans—primary components of poultry feed—skyrocketed due to several factors, including:
- Droughts in key regions like the U.S. Midwest and Brazil, which reduced corn and soybean yields.
- Increased demand for feed grains from China as it rebuilt its hog industry following the African Swine Fever outbreak.
As a result, poultry producers worldwide faced significantly higher feed costs. For instance, the price of corn in the U.S. increased by over 50% from the previous year, which led to substantial increases in production costs for poultry farmers. In response, poultry spot prices also rose as producers passed on the higher costs to retailers and consumers.
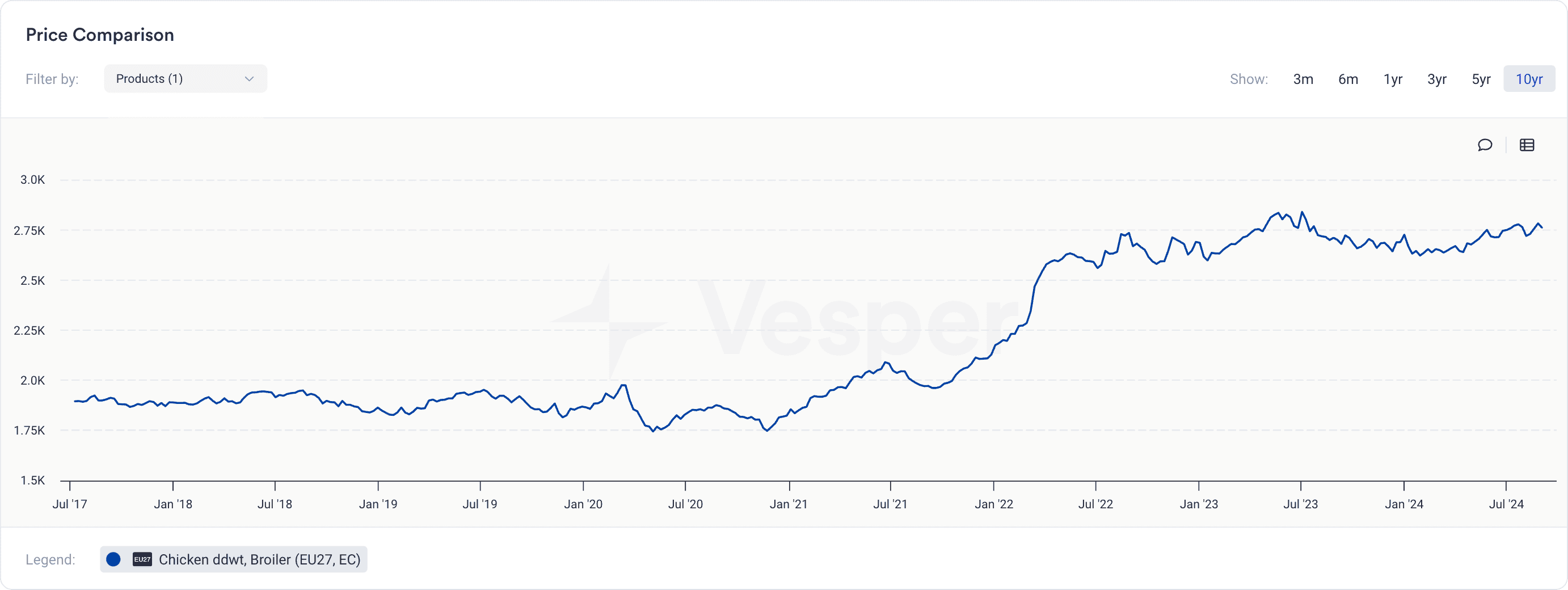
Similarly, poultry producers in the EU experienced a 20-30% rise in production costs due to soaring feed prices, as shown in the Vesper pricing widget below.
2022-2023 Avian Influenza in Europe
Another notable example of avian influenza is the highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) outbreak that affected Europe in 2022 and 2023. Countries like France, the Netherlands, and the UK experienced severe outbreaks, leading to the culling of millions of birds. In France alone, over 20 million birds were culled during this period.
France’s chicken prices saw an increase of over 20% in some regions as the supply of poultry was drastically reduced. This had a ripple effect across the EU, where other countries experienced higher prices for chicken and eggs due to the limited supply. Combined with rising energy and labor costs, this kept prices elevated, as shown in the figure above.
How Do Consumer Trends Influence Poultry Spot Prices?
In recent years, there has been a noticeable shift in consumer demand for higher-quality and ethically sourced poultry products, such as free-range and organic options. These products come with higher production costs, as they often require more space, better feed, and improved living conditions for the birds. These factors result in higher poultry spot prices for these premium segments. This shift is driven by factors such as:
- Animal Welfare Concerns: Consumers are increasingly concerned about the living conditions of animals, especially in intensive farming systems. They prefer poultry that has been raised in environments with more space, access to the outdoors, and fewer interventions like antibiotics.
- Health and Wellness: Organic and free-range poultry is perceived as healthier due to the absence of synthetic chemicals, growth hormones, and antibiotics. Many health-conscious consumers are willing to pay a premium for these products, believing them to be safer and more nutritious.
- Environmental Sustainability: Ethical farming practices are often seen as more sustainable. Free-range and organic poultry farms typically use more environmentally friendly methods, such as rotating pastures and reducing the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which resonates with eco-conscious consumers.
These evolving consumer preferences have a direct influence on poultry spot prices in the following ways:
Higher Production Costs
- Space Requirements: Free-range and organic poultry must be raised in environments that allow for more space and outdoor access. This means fewer birds can be raised per square meter compared to conventional poultry systems, which operate with higher stocking densities. As a result, the cost per bird is higher, and producers pass on these costs to buyers, leading to elevated spot prices.
- Feed Quality: Organic poultry must be fed organic-certified feed, which is significantly more expensive than conventional feed. Organic feed often comes from crops that are grown without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides, which makes it more costly to produce. Additionally, free-range poultry might be allowed to forage for some of their food, which adds variability in growth rates, further increasing the costs of production.
- Longer Growing Periods: Free-range and organic poultry generally have longer growing periods compared to conventional birds that are bred for rapid growth. Slower-growing breeds used in free-range systems take longer to reach market weight, resulting in higher labor, feed, and overhead costs for farmers. This longer cycle increases the overall production cost per bird, which translates into higher spot prices for these products.
Premium Pricing for Ethical Labels
- Organic Certification: Products labeled as organic must adhere to strict regulatory standards, which include using organic feed, prohibiting the use of antibiotics, and providing access to the outdoors. The costs of obtaining and maintaining organic certification are substantial, which is reflected in the final price of organic poultry. Consumers seeking organic products are often willing to pay a higher price, which raises the spot price of organic poultry.
- Free-Range Labels: Similarly, free-range poultry, which is marketed as having more natural living conditions, fetches higher prices in the market. Consumers perceive free-range poultry as more humane and higher in quality, which creates a separate premium market. As the demand for these products increases, their spot prices rise in line with consumer willingness to pay for perceived better quality and welfare standards.
Supply and Demand Imbalance
- Niche Market: Free-range and organic poultry still make up a relatively small portion of the overall poultry market. As a result, supply is more limited compared to conventionally raised poultry. This creates a supply-demand imbalance, especially during periods of high demand such as holidays or seasonal trends, leading to significant spikes in spot prices.
- Limited Production Capacity: Not all poultry producers can or are willing to transition to free-range or organic systems due to the higher costs and stricter regulations. This limits the overall supply of these premium products. When demand outstrips supply, as often happens in the case of organic or free-range poultry, spot prices rise accordingly.
Seasonal and Regional Variations
- Holiday Demand: During holidays like Thanksgiving or Christmas, demand for premium poultry products, particularly organic or free-range turkeys and chickens, increases sharply. This seasonal demand surge drives up spot prices as consumers are willing to pay more for higher-quality poultry for special occasions.
- Regional Preferences: In some regions, there is a stronger preference for ethically sourced poultry. For instance, in parts of Europe, consumer demand for organic and free-range poultry is much higher than in other regions like North America. In these regions, spot prices for free-range and organic poultry can be significantly higher compared to conventional poultry, reflecting regional consumer trends.
Where to Find Poultry Spot Prices
For businesses involved in the poultry supply chain—whether you’re a producer, trader, or buyer—access to accurate and up-to-date poultry spot prices is crucial. Spot prices provide a real-time snapshot of the market, helping you make informed decisions about buying, selling, and managing inventory. Below are several trusted sources where you can find reliable poultry spot prices:
1. Vesper
Vesper offers an intuitive platform providing up-to-date data on poultry spot prices, including detailed insights into specific regions and products. Vesper covers poultry prices such as Chicken (Broilers, Breasts, Legs) and Eggs, with real-time price comparisons for various markets like the EU, U.S., and other global regions. Vesper’s platform also allows users to compare historical price trends, providing a valuable tool for predicting market movements and making strategic purchasing decisions.
2. USDA Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS)
The USDA Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS) provides daily and weekly reports on poultry prices in the United States, including detailed information on wholesale and retail markets. These reports cover various types of poultry, including whole chickens, broilers, turkey, and eggs. The USDA also offers regional breakdowns and provides market trends, which can be invaluable for domestic producers and buyers.
3. European Commission Market Observatory for Meat
The European Commission Market Observatory regularly updates spot prices for poultry in the European Union. This platform provides reports on poultry prices across EU member states, including details on broilers, hens, and eggs. Users can view price trends over different time periods and analyze how specific events, such as trade policies or outbreaks of avian influenza, affect the market.